SDG 6: Ensure availability and sustainable management of water and sanitation for all

Targets
- By 2030, achieve universal and equitable access to safe and affordable drinking water for all.
- By 2030, achieve access to adequate and equitable sanitation and hygiene for all and end open defecation, paying special attention to the needs of women and girls and those in vulnerable situations.
- By 2030, improve water quality by reducing pollution, eliminating dumping and minimizing release of hazardous chemicals and materials, halving the proportion of untreated wastewater and substantially increasing recycling and safe reuse globally.
- By 2030, substantially increase water-use efficiency across all sectors and ensure sustainable withdrawals and supply of freshwater to address water scarcity and substantially reduce the number of people suffering from water scarcity.
- By 2030, implement integrated water resources management at all levels, including through transboundary cooperation as appropriate.
- By 2020, protect and restore water-related ecosystems, including mountains, forests, wetlands, rivers, aquifers and lakes.
- By 2030, expand international cooperation and capacity-building support to developing countries in water- and sanitation-related activities and programmes, including water harvesting, desalination, water efficiency, wastewater treatment, recycling and reuse technologies.
- Support and strengthen the participation of local communities in improving water and sanitation management.
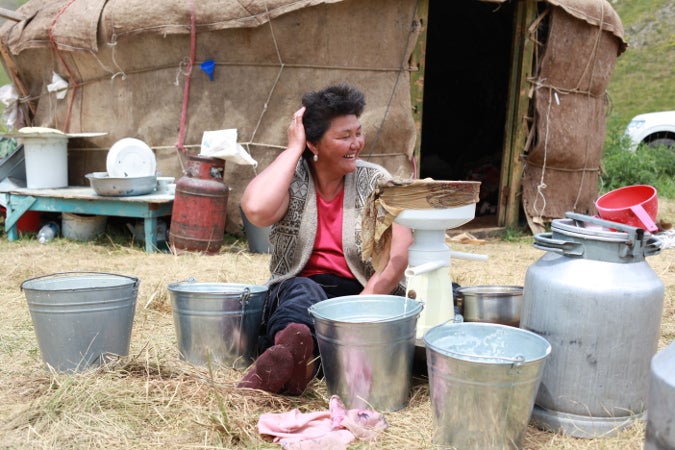
Water sustains life, but too often, for too many people, it is not safe to drink or readily available. In 80 per cent of households with water shortages, women and girls are responsible for water collection. This often means travelling long distances and carrying heavy loads, in some cases with a high risk of violence. The time required can pull girls out of school and leave women with fewer options to earn an income.
The lack of water and sanitation has far-reaching health consequences. When it results in household members falling ill, women assume more of the burden of care and face additional health threats such as from trachoma, which is associated with poor hygiene and can cause blindness. During childbirth, clean water and sanitation can mean the difference between life and death for both mothers and babies.
Billions of people around the world have gained access to safe water and sanitation in recent decades. Climate change and pollution, however, have intensified stress on water sources. In 2015, 2.1 billion people lacked access to safely managed drinking water services. Many still rely on sources like unprotected wells and springs. Around 2.4 billion people use unimproved sanitation facilities that can pollute water and spread disease.[1]
UN Women acts to provide water and sanitation to all by helping governments craft policies and programmes that respond to women’s needs and underpin sustainable services. These include measures that facilitate easy access to safe drinking water so that women have more time to earn an income, girls are more likely to attend school, and family health and hygiene improve.
Stories
From where I stand: Surayo Mirzoyeva
Surayo Mirzoyeva, 41, took part in a self-help group supported by the UN Women project “Empowering abandoned wives of migrant workers in Tajikistan,” which has provided more than 3000 villagers in Fathobod Tajikistan with clean drinking water.
UN Women stresses women’s role in water management at the Water for Life Conference
Over 900 government representatives of UN Member States, experts, academics, and members of international, civil society and private sector organizations from more than 100 countries gathered in Dushanbe, Tajikistan, from 9-10 June to review the Implementation of the International Decade for Action “Water For Life” (2005-2015), a global initiative for international cooperation in water management launched by the Government of Tajikistan 10 years ago.

